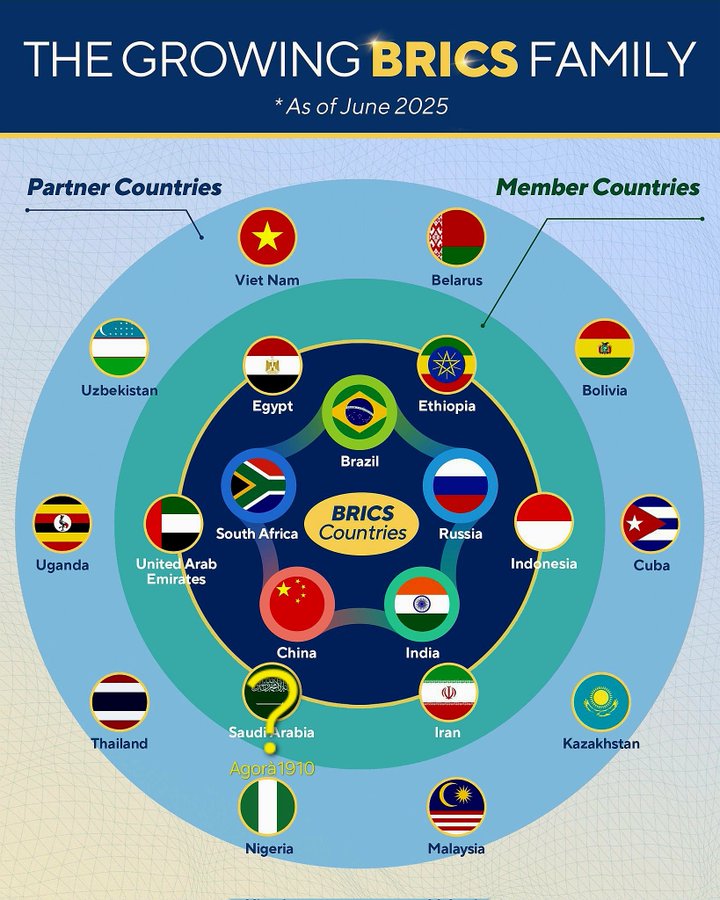
BRICS is a group of eleven countries: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, Ethiopia, Indonesia, and Iran. These nations form a powerful political and diplomatic forum for the Global South. They coordinate on key international issues and work together in diverse areas like trade, finance, governance, and development.
BRICS Objectives
BRICS aims to strengthen economic, political, and social cooperation. It promotes a more balanced and representative global order. Member countries work to reform global institutions like the UN, IMF, World Bank, and WTO. They advocate for sustainable growth, social inclusion, and fair international governance.
History and Origins
The term “BRIC” was coined in 2001 by a Goldman Sachs economist to highlight the rising economic power of Brazil, Russia, India, and China. These four countries later took political initiative to form a forum for dialogue and global cooperation.
The first BRICS meeting took place in 2006 at the UN General Assembly. In 2009, the first official summit of BRICS leaders happened in Ekaterinburg, Russia. In 2011, South Africa joined, changing the name to BRICS.
The 2008 global financial crisis united BRICS countries in calling for reforms in international financial institutions. They gained more influence in global economic governance through coordinated action in forums like the G20 and the IMF.
BRICS Expansion
In 2023, BRICS expanded again. The Johannesburg Summit welcomed six new members: Egypt, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The group now has eleven full members.
Member Countries
currently includes:
- Founding Members (2006–2009): Brazil, Russia, India, China
- Joined in 2011: South Africa
- Joined in 2024: Egypt, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates
Partner Countries
The 2024 Kazan Summit introduced the partner category. The current partners are:
Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Nigeria, Thailand, Uganda, Uzbekistan, and Vietnam.
Vietnam joined in 2025, becoming the 10th partner. With nearly 100 million people and a strong economy, Vietnam brings valuable experience in global trade and South-South cooperation.
Presidency
BRICS rotates its presidency annually based on its name. Brazil holds the presidency in 2025. Each presidency starts on January 1 and ends on December 31. The country in charge sets the year’s priorities and hosts the annual BRICS Summit. With new members added in 2024, BRICS will discuss an updated rotation system.
Participation Categories
BRICS includes two categories of participation:
- Members: Full participants in all meetings.
- Partners: Invited to key meetings like the Leaders’ Summit and Foreign Ministers’ sessions. Participation in other forums depends on consensus.
In 2024, over 30 countries expressed interest in joining BRICS as either members or partners.
- Outreach: Started in 2013 by South Africa. It involves countries from the region of the current BRICS presidency.
- BRICS Plus: Launched by China in 2017. It includes non-regional countries invited to collaborate with.
Suriname Parliament Election: newly found offshore oil at the centre
Burundi Parliament Election: Ruling Party Wins All Parliamentary Seats
Celebrating the ‘International Day of Parliamentarism’ or ‘World Parliament Day’, on June 30